‘We Are Developing Technologies to Support People and Strengthen the Intellect’
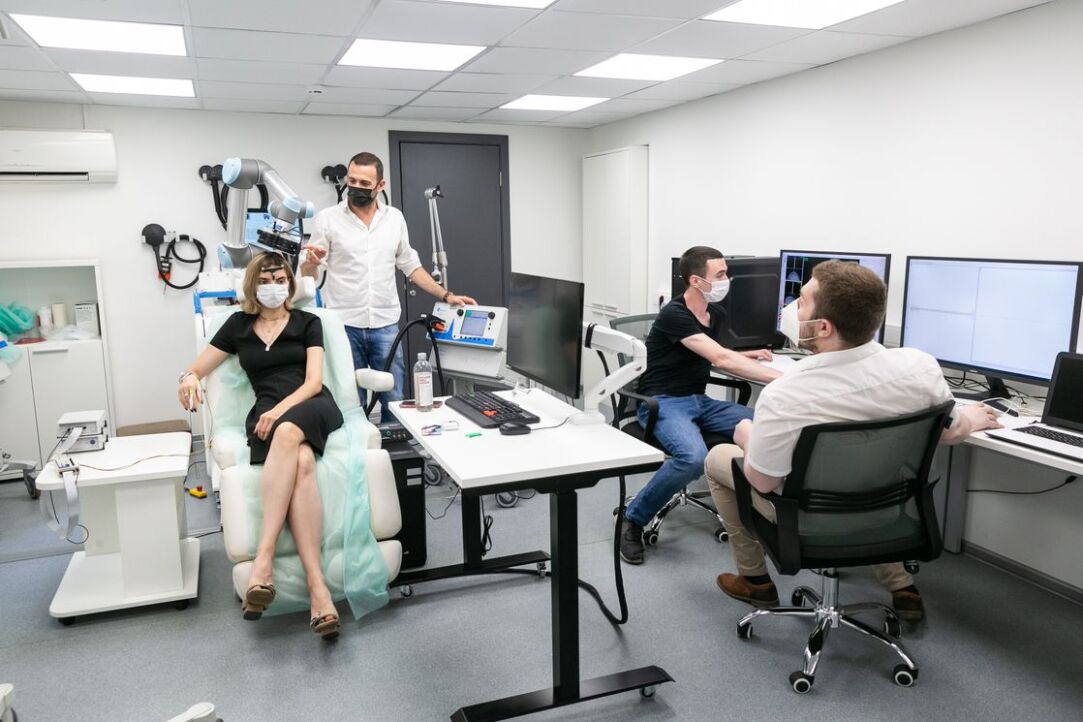

HSE News Service spoke to Director of the Institute of Cognitive Neurosciences, Head of the Centre for Cognition and Decision Making at HSE University, Anna Shestakova about the achievements and goals of the new HSE University’s strategic project ‘Human Brain Resilience: Neurocognitive Technologies for Adaptation, Learning, Development, and Rehabilitation in a Changing Environment’.

— Please tell us how the project idea came about, who initiated it, and how the team was formed.
— It was launched in the spring of this year, and was preceded by a great deal of work. We, like all divisions, participated in the initial competition for strategic projects. Taking into account the growing interest in the achievements of the brain sciences and the importance of developing new neurotechnologies, together with the Centre for Language and Brain, the Faculty of Computer Science, and the Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology, as well as partner laboratories at HSE University in St. Petersburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Perm, we began to form a multidisciplinary project with the apposite name of ‘The Resilient Brain’.
The Institute for Cognitive Neurosciences (ICN) and the Centre for Language and Brain (CNB) are unique scientific divisions demonstrating outstanding world-class results both in the field of studying the neurobiological foundations of brain activity and in the field of diagnosis and rehabilitation of cognitive impairments and disorders.
We study the brain mechanisms of decision-making, memory, attention, speech, body-brain interaction, and cognitive reserve; we are engaged in the neuromodelling of brain processes, creating algorithms for artificial and extended natural intelligence for a wide range of cognitive tasks, developing brain signal decoding programmes and multimodal neuroimaging, neurofeedback, speech diagnostics neurotechnologies, stimulation-free preoperative mapping, and much more.
Psychologists, linguists, mathematicians, physicists and engineers, doctors and biologists—together we are developing neurotechnologies using augmented intelligence aimed at improving the quality of human life and expanding cognitive functions.
— What are the project goals and objectives?
— There are three of them: fundamental, applied and educational.
Scientific discoveries about the functioning of the human brain, as well as neurotechnologies developed as a result of these advances, will be significant for many priority areas. The concepts and tools developed can be used to respond to the key challenges of modern reality: the need for rapid adaptation and learning in a changing situation, population aging, and an increase in the number of neuropsychiatric diseases. The biomedical tools we develop can be implemented in various areas of healthcare and improve its manufacturability based on the principles of a personalised approach. The resulting computational solutions based on the work of the human brain will be able to advance research in the field of artificial and extended natural intelligence.
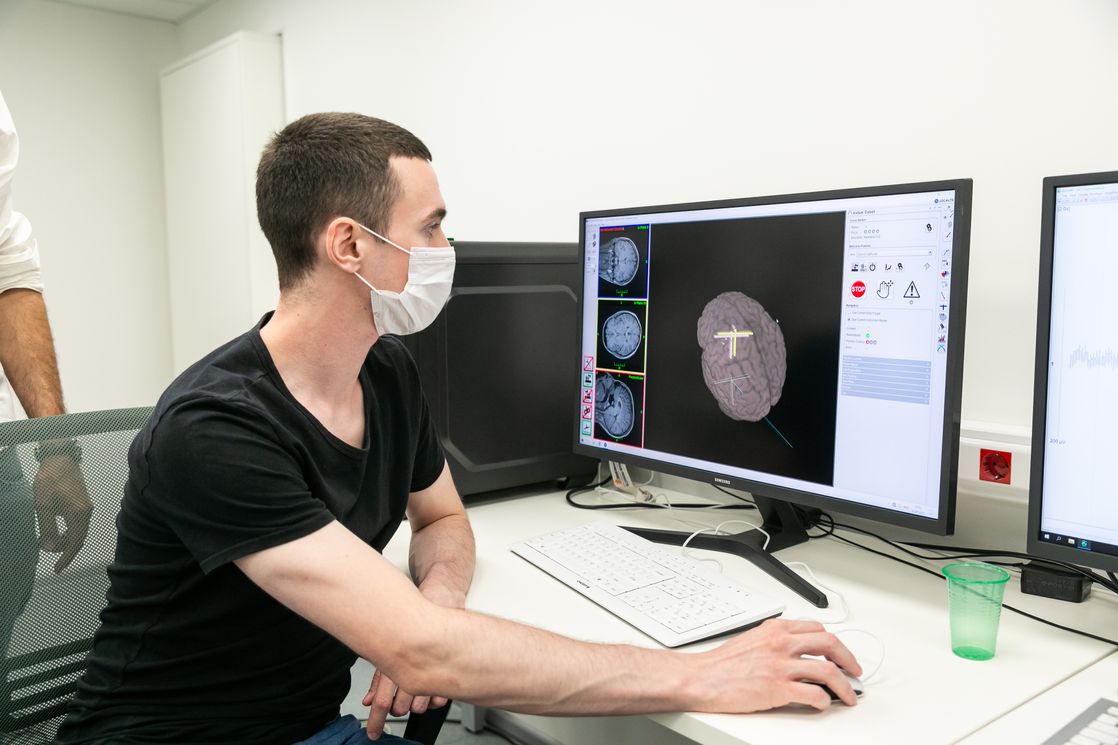
Neurotechnologies for the correction of speech disorders are being developed by CNM under the guidance of its Director Olga Dragoy. Computerised game tools for correcting children’s learning difficulties (in particular, reading) in the language sphere are also being advanced there.
Under the leadership of Alexey Ossadtchi, together with LIFT (a new centre for biomedical technologies), a unique new-generation non-contact encephalography technology using optical magnetometry is being developed.
Finally, within the project’s framework, technologies for the neuroprediction of market behaviour and neurocognitive technologies for optimising urban spaces are under development.
— What is the project's main peculiarity, its uniqueness?
— The focus on augmented intelligence as the antithesis of artificial intelligence: to put people first and technology second. This is very important, because in the world of new technologies, one should understand how the human intellect works and what the brain mechanisms are in order to create new technologies to improve the abilities of the brain and the human.
— What scientific works formed the basis of the proposed solutions?
— Our consortium is, first and foremost, a team of outstanding world-famous scientists who are able to captivate young people with scientific and applied problems at the forefront of science and neurotechnologies. ICH employees annually publish around 50 papers in leading international journals, including NeuroImage, Human Brain Mapping, Stroke, JNeuroisci, PNAS, PLOS Biology, and many others. HSE University employs outstanding specialists in the field of studying the neurocognitive mechanisms of human cognition, and each of them is a unique researcher in their field.
— What results are expected to be obtained after the project implementation and what has been done so far?
— The results include technologies for the development of programmes for correcting speech disorders, as well as applications and games for children. These are also tools for biomedicine: passive preoperative non-invasive mapping without stimulation for brain surgery, new neuroimaging technologies, next-generation encephalography, new neurostimulation protocols, and much more.
The project partners have accumulated impressive experience in the implementation of applied research. FCS scientists are the authors of mathematical methods that can be applied to the study of natural and augmented natural intelligence.
— How often is it possible to use scientific approaches in the solution of applied problems?
— Almost always, the transfer of research into technology is a global trend. However, it is important to note that not every fundamental result can be applied to the solution of specific problems, in our case, those related to the rehabilitation and diagnosis of various pathologies.
— Do you think it is possible to broadly use technology to enhance/strengthen the physical and cognitive abilities of a human in the near future?
— Thanks to the growth of computer technology and AI, the development and implementation of technologies such as neuro- and biofeedback and brain-computer interfaces have accelerated remarkably and are already being used in medicine and education.
Neurofeedback technology (NFB) is a neuromodulation technology that allows a person to control the activity of their own brain. Within the framework of this approach, signals of brain activity are analysed in real time and parameters characterising brain activity are calculated, then information about it is presented to the user. The use of the NFB allows the user to learn self-regulation skills, including the conscious regulation of brain activity.

— Is it possible to apply your developments in the prevention and treatment of diseases and, possibly, the prevention of deviant behaviour?
— Most of our work is aimed at studying the mechanisms of decision-making, visual and auditory perception, their norm and pathology. For example, in Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia and autism, certain cognitive functions are impaired. If we know how the brain provides a particular function and how its implementation differs in pathology, we can diagnose disorders and even point out abnormalities in the brain with certain problems.
— What departments and research groups are involved in the project outside of HSE University?
— These are all medical universities, research medical institutions; they are all tied to the development of biomedical technologies.
— How will the project contribute to the development of the university?
— One can call it a new direction in the natural sciences. It is a project with an emphasis on the natural sciences. We are entering the biomedical research market, and this is important for the reputation of HSE University as a multidisciplinary university.
The project has several tasks, including the creation of unique educational tracks. The key educational initiative is the Master’s programme ‘Cognitive Sciences and Technologies: From Neuron to Cognition’, which is very popular among HSE University applicants. For the second year, the new Bachelor’s programme ‘Cognitive Neurobiology’ on the basis of the Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology (supervised by Olga Martynova) is welcoming new applicants.
Thanks to the effort of ICN, a new cross-disciplinary graduate school in cognitive science has emerged.
We have become trendsetters in creating new areas of education, for example, the cross-cutting track ‘bachelor’s degree —master’s degree—postgraduate studies.’
The annual school on active and passive methods of neuromapping led by Matteo Feurra and Evgeny Blagoveshchensky is also enjoying great success.
See also:
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
Designing an Accurate Reading Skills Test: Why Parallel Texts are Important in Dyslexia Diagnosis
Researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed a tool for accurately assessing reading skills in adults with reading impairments. It can be used, for instance, before and after sessions with a language therapist. The tool includes two texts that differ in content but are equal in complexity: participants were observed to read them at the same speed, make a similar number of errors, and understand the content to the same degree. Such parallel texts will enable more accurate diagnosis of dyslexia and better monitoring of the effectiveness of interventions aimed at addressing it. The paper has been published in Educational Studies.
Internal Clock: How Heart Rate and Emotions Shape Our Perception of Time
Our perception of time depends on heart rate—this is the conclusion reached by neuroscientists at HSE University. In their experiment, volunteers watched short videos designed to evoke specific emotions and estimated each video's duration, while researchers recorded their heart activity using ECG. The study found that the slower a participant's heart rate, the shorter they perceived the video to be—especially when watching unpleasant content. The study has been published in Frontiers in Psychology.
Intellectual Capital in the Face of Shocks: Russia and Iran Explore Internationalisation
In today's issue of Schola, Mariya Molodchik, Senior Research Fellow at the International Laboratory of Intangible-Driven Economy and Professor at the School of Economics and Finance at HSE University’s Campus in Perm, discusses a joint project with Iran University of Science and Technology, titled 'Internationalization of Companies from Developing Countries: The Role of Intellectual Resources in Response to Exogenous Shocks.'
HSE Researchers Introduce Novel Symmetry-Aware Neural Network Architecture
Researchers at the HSE Laboratory for Geometric Algebra and Applications have developed a new neural network architecture that can accelerate and streamline data analysis in physics, biology, and engineering. The scientists presented their solution on July 16 in Vancouver at ICML 2025, one of the world's leading conferences on machine learning. Both the paper and the source code are publicly available.
Students from HSE and Other Universities Carry Out Research Expedition at New Chersonesos
As part of the Rediscovering Russia student expedition programme, HSE University organised a research trip under the framework of the School for Young Humanities Scholars to the New Chersonesos museum and church complex in Sevastopol. The results of this expedition will form the basis for proposals on educational projects aimed at shaping young people’s historical memory of the role of Chersonesos, Crimea, and the Byzantine legacy in the history of Russian culture and statehood.
HSE Researchers Determine Frequency of Genetic Mutations in People with Pulmonary Hypertension
For the first time in Russia, a team of scientists and clinicians has conducted a large-scale genetic study of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. The team, which included researchers from the International Laboratory of Bioinformatics at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science, analysed the genomes of over a hundred patients and found that approximately one in ten carried pathogenic mutations in the BMPR2 gene, which is responsible for vascular growth. Three of these mutations were described for the first time. The study has been published in Respiratory Research.
First Caucasus School on Experimental Research and Cognitive Sciences Takes Places in Adygea
On September 17–20, 2025, the First Caucasus School on Experimental Research and Cognitive Sciences took place at the Gornaya Legenda venue of Adyghe State University (ASU). The event was organised by the ASU Experimental Linguistics Laboratory, the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, and the HSE Centre for Sociocultural and Ethnolinguistic Studies. The school brought together over 50 participants—students, doctoral candidates, and early-career researchers from across Russia, along with lecturers and speakers from France, Serbia, China, Turkey, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan.
HSE Scientists Reveal How Disrupted Brain Connectivity Affects Cognitive and Social Behaviour in Children with Autism
An international team of scientists, including researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, has for the first time studied the connectivity between the brain's sensorimotor and cognitive control networks in children with autism. Using fMRI data, the researchers found that connections within the cognitive control network (responsible for attention and inhibitory control) are weakened, while connections between this network and the sensorimotor network (responsible for movement and sensory processing) are, by contrast, excessively strong. These features manifest as difficulties in social interaction and behavioural regulation in children. The study has been published in Brain Imaging and Behavior.
Scientists Develop New Method to Detect Motor Disorders Using 3D Objects
Researchers at HSE University have developed a new methodological approach to studying motor planning and execution. By using 3D-printed objects and an infrared tracking system, they demonstrated that the brain initiates the planning process even before movement begins. This approach may eventually aid in the assessment and treatment of patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s. The paper has been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.