First Digital Adult Reading Test Available on RuStore
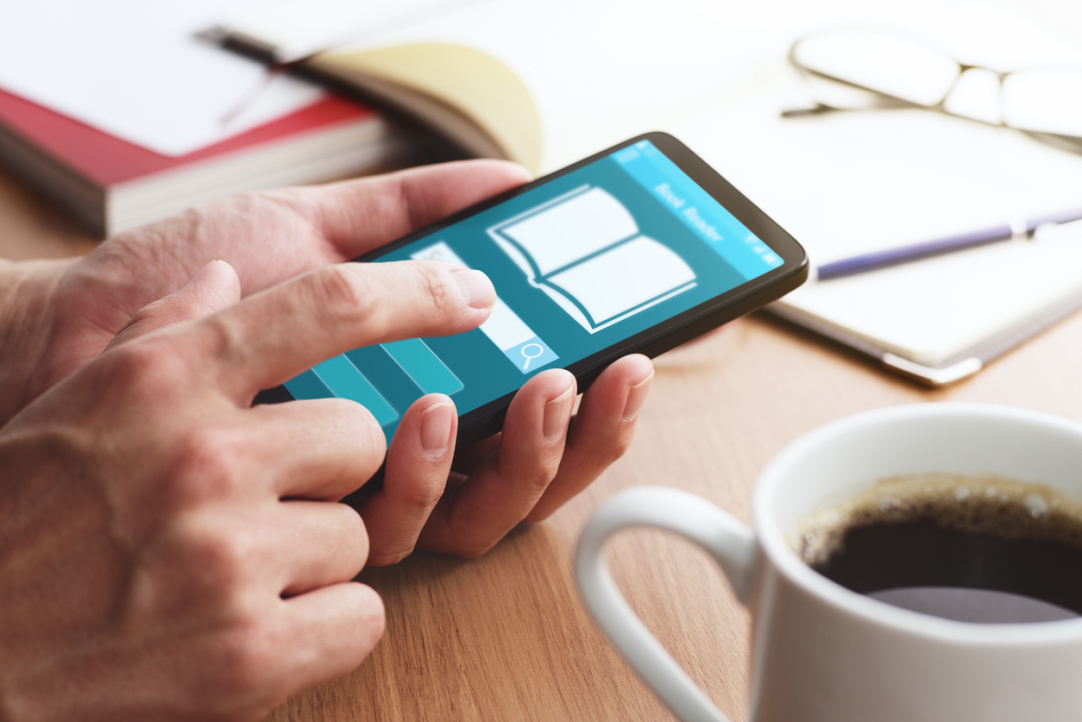

HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain has developed the first standardised tool for assessing Russian reading skills in adults—the LexiMetr-A test. The test is now available digitally on the RuStore platform. This application allows for a quick and effective diagnosis of reading disorders, including dyslexia, in people aged 18 and older.
Reading skills are essential for a social and professional life. For millions of adults with reading impairments, the lack of a timely diagnosis can mean inaccessibility to quality education, career opportunities, and social support. However, for adults in Russia, there was no reliable tool or standard for objectively measuring reading proficiency or comparing results with normative data. The LexiMetr-A digital test fills this gap, offering professionals and researchers an effective way to assess the speed and accuracy of reading, as well as the level of reading comprehension.

Svetlana Dorofeeva
‘The development of LexiMetr-A was a logical consequence of our efforts to create linguistics-based tests for diagnosing speech and reading disorders in children. Adults with reading impairments also need age-appropriate tools,’ says Svetlana Dorofeeva, one of test developers and researcher at HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain.
The test has two parallel versions, one for initial diagnostics and the other for retesting or for assessing the effectiveness of interventions. The versions are balanced in terms of a number of psycholinguistic parameters, such as the length of words in syllables and in letters, the frequency of words, and the complexity of syntactic structures. Each text comes with a set of reading comprehension questions. After reading and marking errors, the application automatically calculates reading parameters and provides information about which syntactic structures were the most difficult. This level of detail is particularly useful for planning remedial work.
The application is aimed at specialists: speech therapists, neuropsychologists, and neurologists working in clinics, educational and research institutions. It includes age-appropriate cutoff levels for different user groups from 18 to 60+ years old, which ensures high diagnostic accuracy. The app replaces paper protocols, manual error counting, and voice recorders. All stages of the test—from text demonstration to error analysis—take place in a digital interface. The results, including audio recordings and markings, are uploaded in a useful format, making it easier to observe and draw conclusions.
The tool will enable informed decisions for selecting a future approach to working with reading difficulties or supporting adults with dyslexia. For instance, a confirmed dyslexia diagnosis could be taken into account by universities when determining a specific assessment system for students with such difficulties.
The developers emphasise that the test will be useful in both clinical and scientific application. The new tool collects an array of audio data and reading indicators, making it a valuable research tool for cognitive linguistics, psycholinguistics, and neuropsychology.

Olga Dragoy
‘Our goal is to make reading diagnostics more accessible and up-to-date. LexiMetr-A is not just a test; it is a practical tool that saves time, provides accurate results, and opens up new possibilities for helping people with dyslexia,’ comments Olga Dragoy, Director of the Centre for Language and Brain, HSE University.
See also:
Banking Crises Drive Biodiversity Loss
Economists from HSE University, MGIMO University, and Bocconi University have found that financial crises have a significant negative impact on biodiversity and the environment. This relationship appears to be bi-directional: as global biodiversity declines, the likelihood of new crises increases. The study examines the status of populations encompassing thousands of species worldwide over the past 50 years. The article has been published in Economics Letters, an international journal.
Scientists Discover That the Brain Responds to Others’ Actions as if They Were Its Own
When we watch someone move their finger, our brain doesn’t remain passive. Research conducted by scientists from HSE University and Lausanne University Hospital shows that observing movement activates the motor cortex as if we were performing the action ourselves—while simultaneously ‘silencing’ unnecessary muscles. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.
Russian Scientists Investigate Age-Related Differences in Brain Damage Volume Following Childhood Stroke
A team of Russian scientists and clinicians, including Sofya Kulikova from HSE University in Perm, compared the extent and characteristics of brain damage in children who experienced a stroke either within the first four weeks of life or before the age of two. The researchers found that the younger the child, the more extensive the brain damage—particularly in the frontal and parietal lobes, which are responsible for movement, language, and thinking. The study, published in Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, provides insights into how age can influence the nature and extent of brain lesions and lays the groundwork for developing personalised rehabilitation programmes for children who experience a stroke early in life.
Scientists Test Asymmetry Between Matter and Antimatter
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has collected and analysed data from dozens of experiments on charm mixing—the process in which an unstable charm meson oscillates between its particle and antiparticle states. These oscillations were observed only four times per thousand decays, fully consistent with the predictions of the Standard Model. This indicates that no signs of new physics have yet been detected in these processes, and if unknown particles do exist, they are likely too heavy to be observed with current equipment. The paper has been published in Physical Review D.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.
Institute for Robotics Systems Established at HSE University
As decided by the HSE University Academic Council, a new Institute for Robotics Systems will be established at HSE, and with a strong fundamental base. It will cooperate with relevant departments across the university and engage students and doctoral candidates in research and development (R&D). First Vice Rector of HSE University and Director of the Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics of Knowledge, Leonid Gokhberg, discussed the expected practical results and the framework for cooperation with an industrial partner.
Scientists Uncover Why Consumers Are Reluctant to Pay for Sugar-Free Products
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have investigated how 'sugar-free' labelling affects consumers’ willingness to pay for such products. It was found that the label has little impact on the products’ appeal due to a trade-off between sweetness and healthiness: on the one hand, the label can deter consumers by implying an inferior taste, while on the other, it signals potential health benefits. The study findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE Seeks New Ideas for AI Agents: Initiative Competition Launched
HSE University is inviting researchers and lecturers to present concepts for new digital products based on artificial intelligence. The best projects will receive expert and technological support. Applications are open until December 19, 2025.
IDLab: Fascinating Research, Tough Deadlines, and Academic Drive
The International Laboratory of Intangible-driven Economy (IDLab) was established at the HSE campus in Perm 11 years ago. Its expertise in data processing and analysis allows researchers to combine fundamental studies with applied projects, including the development of risk and cybersecurity models for Sber. The head of the laboratory, Professor Petr Parshakov, and Senior Research Fellow Professor Mariya Molodchik spoke to the HSE News Service about IDLab’s work.
HSE Lecturers Awarded Yandex ML Prize 2025
The Yandex ML Prize is awarded to lecturers and heads of educational programmes who contribute to the development of artificial intelligence in Russia. This year, 10 laureates were selected from 300 applicants, including three members of the HSE Faculty of Computer Science (FCS). A special Hall of Fame award was also presented for contributions to the establishment of machine learning as an academic field. One of the recipients was Dmitry Vetrov, Research Professor at the HSE FCS.